Australian Firm Unveils First Biocomputer with Human Brain Cells
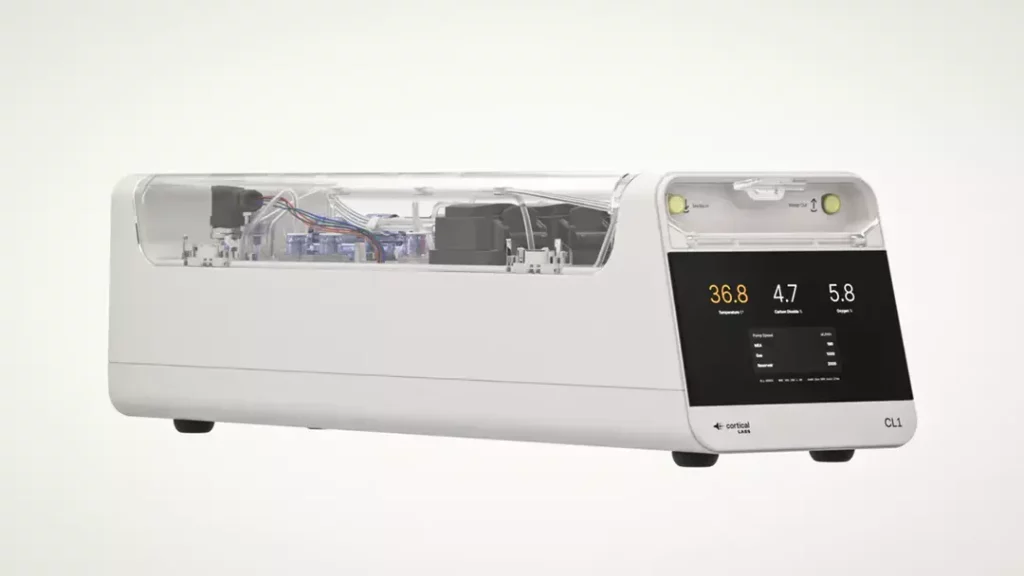
In a groundbreaking development, Australian startup Cortical Labs has launched CL1, the world’s first biological computer combining human brain cells with silicon. Dubbed Synthetic Biological Intelligence (SBI), this innovative technology offers superior adaptability and energy efficiency over traditional Artificial Intelligence (AI). CL1 is available for purchase or as a cloud-based service, which could revolutionize industries such as medicine, robotics, and AI development, raising important ethical and scientific questions along the way.
The emergence of CL1 marks a significant milestone in the evolution of AI, as traditional AI systems rely on complex algorithms and data processing to perform tasks. In contrast, CL1 uses human brain cells, specifically cortical neurons, to process information and make decisions. This biological approach enables the biocomputer to learn and adapt in ways that traditional AI systems cannot, making it a game-changer for various industries.
Cortical Labs, the company behind CL1, has been working on this project for several years, with a team of experts in neuroscience, engineering, and computer science. The company’s CEO, Dr. Matthew Cooper, explains that the goal was to create a system that could mimic the human brain’s ability to learn and adapt. “We wanted to create a system that could learn and change over time, just like the human brain,” Dr. Cooper said in an interview. “By combining human brain cells with silicon, we’ve created a system that’s not only more efficient but also more intelligent and adaptable.”
CL1 is designed to be used in a variety of applications, including medicine, robotics, and AI development. In medicine, CL1 could be used to develop more accurate and personalized treatments for diseases. For example, the biocomputer could be used to analyze patient data and recommend the most effective treatment options. In robotics, CL1 could be used to create more intelligent and adaptable robots that can learn and adapt to new situations. In AI development, CL1 could be used to create more advanced AI systems that can learn and adapt in ways that traditional AI systems cannot.
The potential applications of CL1 are vast, and the technology has the potential to revolutionize industries across the globe. However, the development of CL1 also raises important ethical and scientific questions. One of the main concerns is the use of human brain cells in the biocomputer. Some experts have raised concerns about the ethics of using human brain cells in this way, and whether it is acceptable to use human tissue for commercial purposes.
Another concern is the potential impact of CL1 on the job market. As AI systems become more advanced, there is a risk that they could replace human workers in certain industries. This could have significant social and economic implications, and it is important that policymakers and business leaders consider these implications when developing and implementing new AI technologies.
In conclusion, the launch of CL1 is a significant milestone in the development of AI, and it has the potential to revolutionize industries across the globe. However, it also raises important ethical and scientific questions that need to be addressed. As we move forward with the development and implementation of CL1, it is essential that we consider the potential implications of this technology and work to address any concerns that arise.