Andhra Pradesh Launches Novel Afforestation Project in Kadapa
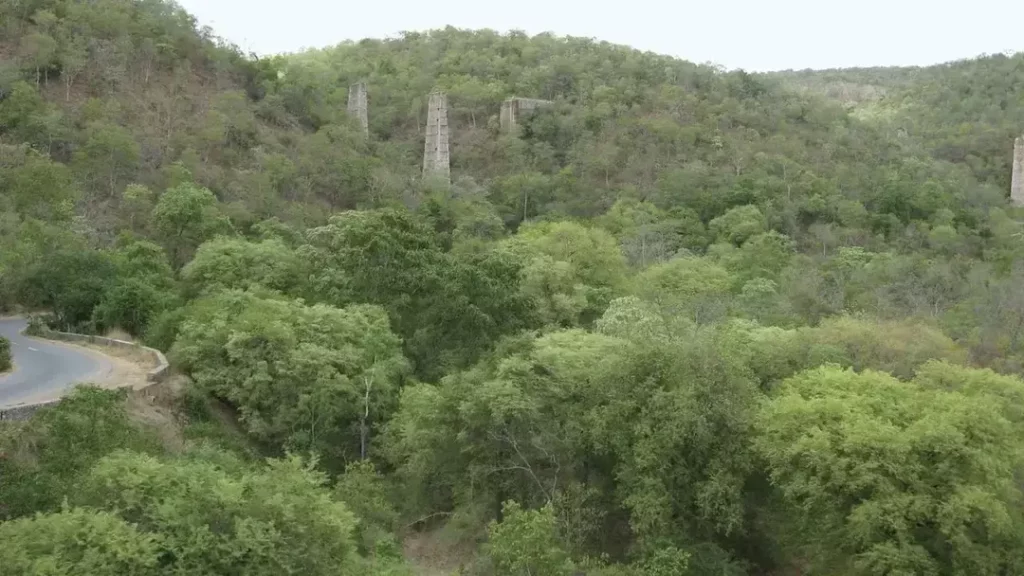
Andhra Pradesh has taken a groundbreaking step in its efforts to combat climate change and ecological degradation by launching the Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project. This innovative initiative is focused on reviving indigenous flora in the ecologically degraded Kadapa district, making it a first-of-its-kind project in the state. Unlike traditional afforestation efforts that rely on exotic species, this project prioritizes ecological restoration, biodiversity, and long-term water security by reintroducing native trees.
The Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project is an ambitious endeavor that aims to restore over 10,000 hectares of degraded forest land in Kadapa district. The project will focus on reintroducing native tree species, which are better adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. This approach not only ensures the survival of native flora but also promotes biodiversity and ecological balance.
The project’s emphasis on ecological restoration is a significant departure from traditional afforestation methods, which often prioritize quantity over quality. These methods typically involve planting a large number of exotic tree species, which may not be well-suited to the local environment. This approach can lead to a range of negative consequences, including reduced biodiversity, decreased ecosystem resilience, and increased water consumption.
By contrast, the Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project is designed to promote ecological restoration and long-term water security. The project will focus on restoring the natural hydrological cycle of the region, which will help to recharge groundwater aquifers and maintain healthy water tables. This approach is critical for ensuring the long-term sustainability of the region’s water resources, particularly in the face of climate change.
The project’s focus on biodiversity and ecological balance is also critical for promoting ecosystem resilience. By reintroducing native tree species and restoring natural habitats, the project will help to support a wide range of plant and animal species. This will not only promote biodiversity but also help to maintain the health and resilience of local ecosystems.
The Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project is a collaborative effort between the Government of Andhra Pradesh, local communities, and international organizations. The project will involve a range of stakeholders, including local farmers, foresters, and environmental organizations. This collaborative approach will help to ensure the project’s success and promote community engagement and ownership.
The project’s goals are ambitious, and its success will depend on careful planning, execution, and monitoring. The project’s organizers will need to carefully select native tree species that are well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions. They will also need to develop effective strategies for maintaining the health and resilience of restored ecosystems, including measures to prevent invasive species and promote ecological balance.
The Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project has the potential to serve as a model for other afforestation efforts in the region. By prioritizing ecological restoration, biodiversity, and long-term water security, the project can help to promote sustainable forest management practices and support the health and resilience of local ecosystems.
In conclusion, the Kadapa Native Forest Restoration Project is a groundbreaking initiative that has the potential to make a significant impact on the region’s ecosystems and communities. By prioritizing ecological restoration, biodiversity, and long-term water security, the project can help to promote sustainable forest management practices and support the health and resilience of local ecosystems.