Earth’s Inner Core is Changing Shape, Say Scientists
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have found that Earth’s inner core is changing shape. This finding has significant implications for our understanding of the Earth’s internal dynamics and the processes that shape our planet. The research, published in the journal Nature, suggests that the liquid flow of the outer core, combined with the uneven gravitational field, may be causing the inner core to deform.
The study, led by a team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego, analyzed seismic wave patterns from earthquakes that occurred repeatedly in the same location between 1991 and 2023. By examining these patterns, the scientists were able to detect subtle changes in the Earth’s inner core over time.
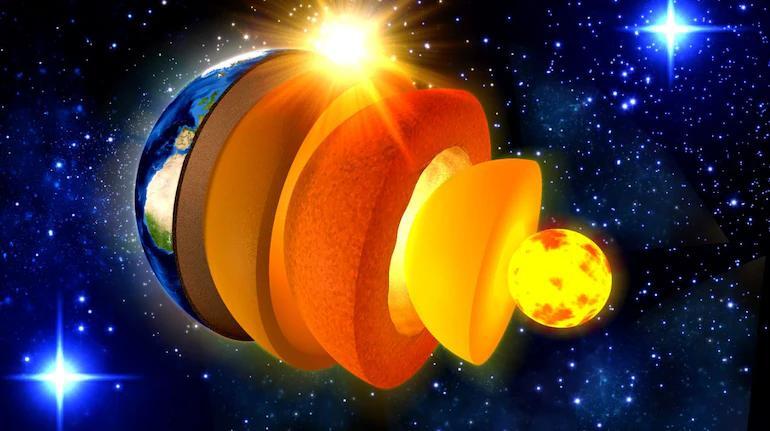
The Earth’s inner core is a solid, iron-nickel alloy at the center of the planet, with a temperature of around 5,000 to 6,000 degrees Celsius. It is surrounded by a liquid outer core, which is made up of a mixture of iron and nickel. The outer core is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field through the movement of molten iron.
The researchers used a technique called seismic tomography to create detailed images of the Earth’s inner core. This involved analyzing the speed and pattern of seismic waves as they traveled through the Earth after an earthquake. By comparing the wave patterns from different earthquakes, the scientists were able to detect changes in the inner core’s shape and structure.
The study found that the inner core has been changing shape over the past three decades, with the equator of the inner core shrinking by about 0.3% since 1991. This means that the inner core has been contracting slightly, with the equatorial region shrinking more than the polar regions.
According to the researchers, the liquid flow of the outer core is likely the main driver of this change. The outer core is constantly moving and circulating, which can cause the inner core to deform. This deformation can occur because the inner core is not perfectly spherical, and the uneven gravitational field of the Earth can cause it to bulge and shrink in different areas.
The researchers also found that the inner core’s changes in shape are not uniform, with some regions expanding or contracting more rapidly than others. This could be due to variations in the flow of the outer core or other internal processes that are not yet fully understood.
The implications of this finding are significant. The Earth’s inner core is thought to play a crucial role in shaping the planet’s magnetic field and geodynamo, which is the process by which the Earth’s core generates its magnetic field. Changes in the inner core’s shape could, therefore, have a significant impact on the Earth’s magnetic field and the planet’s climate.
The study’s findings also provide new insights into the Earth’s internal dynamics and the processes that shape our planet. The researchers suggest that the inner core’s changes in shape could be used as a proxy for studying the Earth’s internal dynamics and understanding the processes that shape the planet’s magnetic field.
In conclusion, the discovery that Earth’s inner core is changing shape is a significant finding that has important implications for our understanding of the Earth’s internal dynamics and the processes that shape our planet. The study’s findings provide new insights into the Earth’s internal dynamics and the processes that shape the planet’s magnetic field, and highlight the importance of continued research into the Earth’s internal dynamics.
Source:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00395-7
Note: The article is based on the research published in the journal Nature, and the findings are subject to peer review and further research.