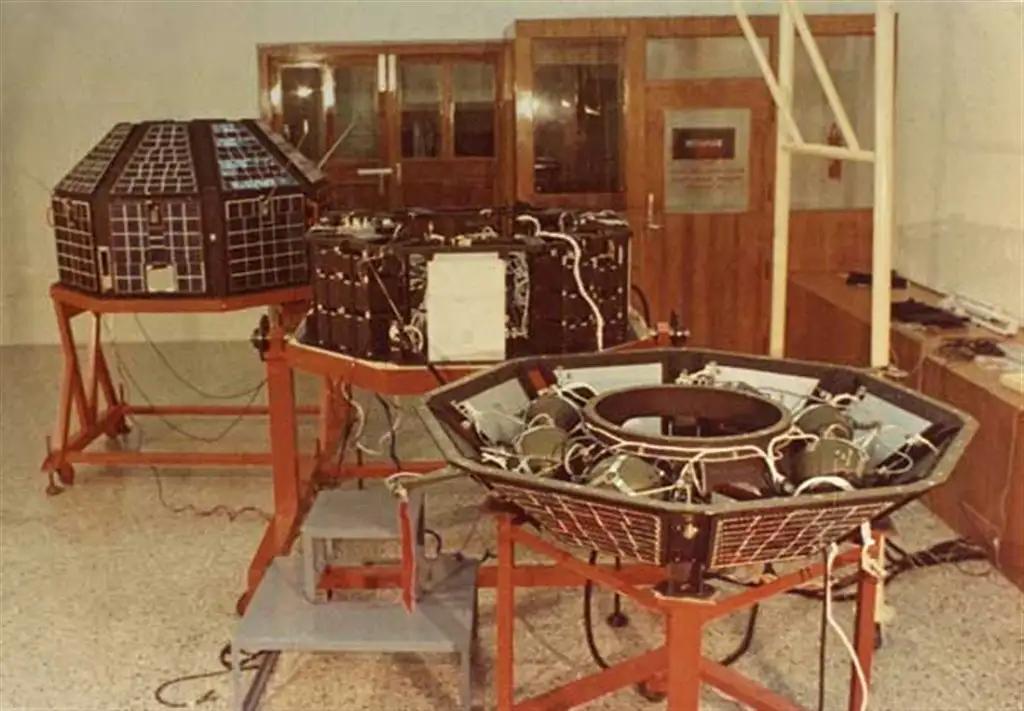
India Launched its First Satellite Aryabhata 50 Years Ago Today
On April 19, 1975, India made history by launching its first satellite, Aryabhata, into space. This momentous occasion marked a significant milestone in the country’s space program, making India the 11th country in the world to send a satellite into orbit. The satellite was completely designed and fabricated in India, and its successful launch was a testament to the country’s growing capabilities in the field of space technology.
Aryabhata was named after an ancient Indian mathematician and astronomer who is credited with being one of the earliest known Indian mathematicians and astronomers. He is believed to have lived in the 5th century CE and is known for his contributions to the field of mathematics, particularly in the area of algebra and arithmetic. The satellite was a fitting tribute to his legacy, and its launch marked a new era in India’s space program.
The satellite was launched by a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar, a rocket launch site located in Russia. The rocket was a reliable and versatile launch vehicle that had been used to launch numerous satellites and spacecraft into space. The launch was a joint effort between India and the Soviet Union, with India responsible for designing and fabricating the satellite, and the Soviet Union providing the launch vehicle and launch services.
Aryabhata was a small satellite, weighing around 360 kilograms (790 pounds), and was designed to operate in a low Earth orbit. The satellite was equipped with a number of instruments, including a payload of 18 kg (40 pounds), which was designed to carry out a variety of scientific experiments. The payload included a number of instruments, such as a cosmic ray detector, a solar X-ray monitor, and a magnetometer, which were designed to study the Earth’s magnetic field, the Sun’s radiation, and the cosmic rays.
The satellite was placed into an orbit with a perigee of 555 kilometers (346 miles) and an apogee of 665 kilometers (413 miles), which was a relatively low orbit for a satellite. The satellite’s orbit was designed to be inclined at an angle of 50 degrees to the equator, which allowed it to study the Earth’s magnetic field and the Sun’s radiation.
Aryabhata was a significant achievement for India’s space program, and its launch marked a new era in the country’s space exploration. The satellite’s successful launch demonstrated India’s capabilities in the field of space technology, and it paved the way for future satellite launches and space missions.
The success of Aryabhata also marked a significant milestone in India’s space program, which was established in the early 1960s. The program was initially focused on launching small satellites and conducting scientific experiments, but it has since grown to become one of the largest and most successful space programs in the world.
Today, India is home to a number of space agencies and organizations, including the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), which is responsible for the country’s space program. ISRO has launched a number of successful satellites and spacecraft, including the Chandrayaan-1 lunar mission, which successfully orbited the Moon in 2008.
In conclusion, the launch of Aryabhata 50 years ago today marked a significant milestone in India’s space program. The satellite’s successful launch demonstrated India’s capabilities in the field of space technology, and it paved the way for future satellite launches and space missions. Aryabhata was a fitting tribute to the legacy of an ancient Indian mathematician and astronomer, and its launch will always be remembered as a significant achievement in India’s space program.






