North America is ‘Dripping’ Down into Earth’s Mantle: Study
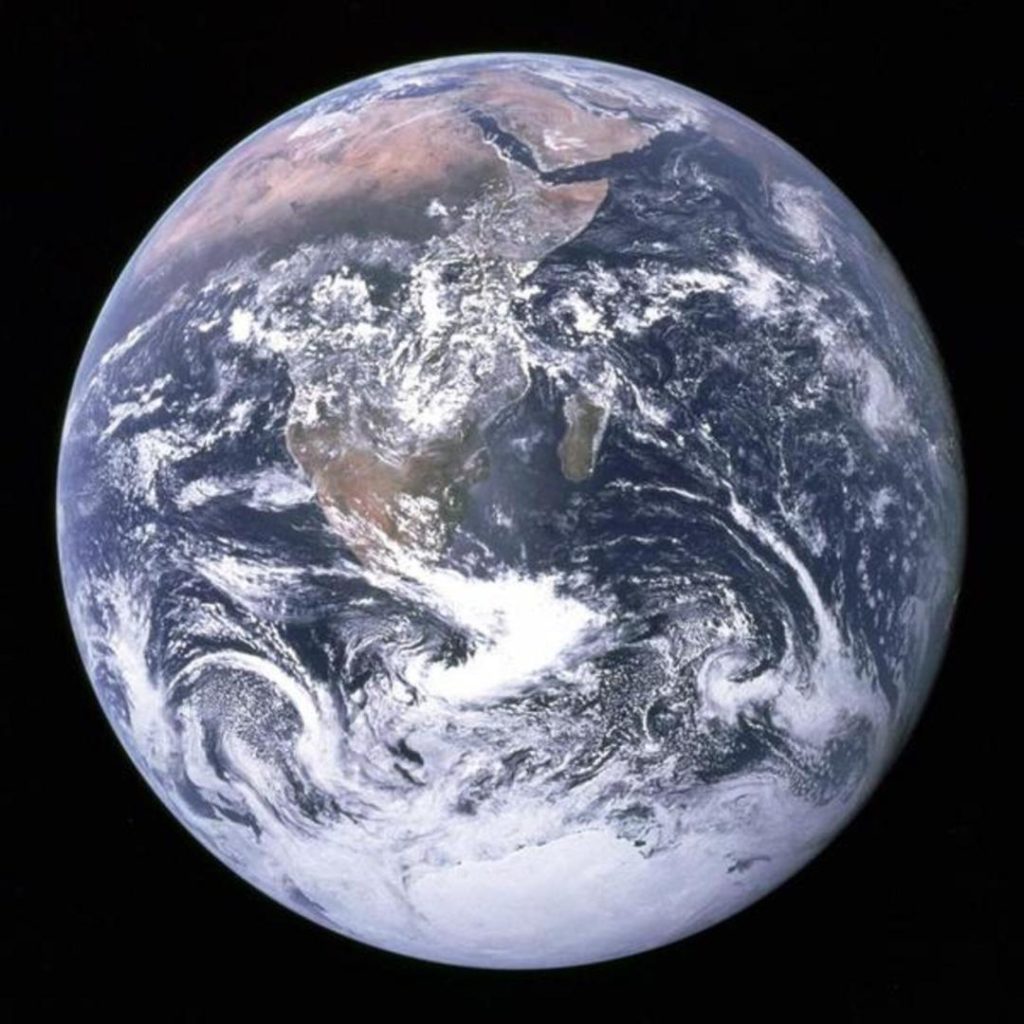
The Earth’s mantle is a vast, hot, and dynamic region beneath our feet, stretching from the crust to a depth of over 2,900 kilometers. For centuries, scientists have been fascinated by the mysteries of the mantle, and recent findings have shed new light on the complex processes that shape our planet. In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Geoscience, researchers have discovered that the underside of the North American continent is “dripping” down into the Earth’s mantle in massive blobs of rock. This phenomenon, known as “cratonic thinning,” is a previously unknown process that is concentrated over the Midwest of the United States.
The Discovery
The study, led by Dr. Simon Kelley of the University of Oxford, analyzed data from the Earth’s mantle and crust, collected over several decades. By combining seismic data, gravity measurements, and laboratory experiments, the researchers were able to create a detailed 3D model of the North American continent. The findings revealed that the crust beneath the Midwest is thinner than previously thought, with some areas stretching as thin as 40 kilometers. This thinning is not uniform, however, and is instead concentrated in large, irregular blobs.
Cratonic Thinning: A New Process
Cratonic thinning is a process that has been observed before, but never in action. It occurs when the Earth’s crust is stretched and thinned, allowing the mantle to rise up and fill the gap. In the case of North America, the process is happening rapidly, with the crust thinning at a rate of several millimeters per year. This is incredibly fast, equivalent to the movement of the continents themselves.
The researchers believe that the cratonic thinning is driven by the movement of the North American tectonic plate, which is being pushed beneath the Pacific plate at a rate of several centimeters per year. As the plate is pushed down, it encounters increasing heat and pressure, causing the rocks to melt and rise up into the mantle.
Implications for Our Understanding of the Earth
The discovery of cratonic thinning has significant implications for our understanding of the Earth’s mantle and crust. It suggests that the processes that shape the Earth’s surface are more complex and dynamic than previously thought, and that the mantle is more involved in the creation of the continents than previously believed.
The study also highlights the importance of the Midwest region in the Earth’s geological history. The area has long been known for its rich mineral deposits, and the new findings suggest that these deposits may be linked to the movement of the tectonic plate.
What This Means for the Future
The discovery of cratonic thinning has significant implications for our understanding of the Earth’s geological future. As the North American plate continues to move, it is likely that the process will continue, potentially leading to further changes in the Earth’s surface.
The study also highlights the importance of continued research into the Earth’s mantle and crust. As new technologies and methods become available, scientists will be able to continue to refine our understanding of the Earth’s internal processes, and uncover new secrets about the planet we call home.
Conclusion
The discovery of cratonic thinning in North America is a significant breakthrough in our understanding of the Earth’s mantle and crust. The study, published in Nature Geoscience, reveals a previously unknown process that is concentrated over the Midwest region of the United States. As scientists continue to study this phenomenon, we can expect to learn more about the complex and dynamic processes that shape our planet.
Source
Kelley, S. et al. (2025). Cratonic thinning in the North American continent. Nature Geoscience, 1-9. doi: 10.1038/s41561-025-01671-x