Title: Toothpaste-like Battery That Can Take Any Shape Developed by Scientists
In a groundbreaking innovation, scientists at Linköping University in Sweden have created a new type of battery that resembles toothpaste in texture and can take any shape. This malleable battery is made from conductive plastics and lignin, a sustainable byproduct from paper production, and has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about battery design and functionality.
The team of researchers, led by Aiman Rahmanudin, used a combination of conductive plastics and lignin to create the unique battery material. Lignin is a natural polymer found in plant cell walls, and is often discarded as a waste product in the paper-making process. By using lignin as a key component, the scientists were able to create a biodegradable and sustainable battery material.
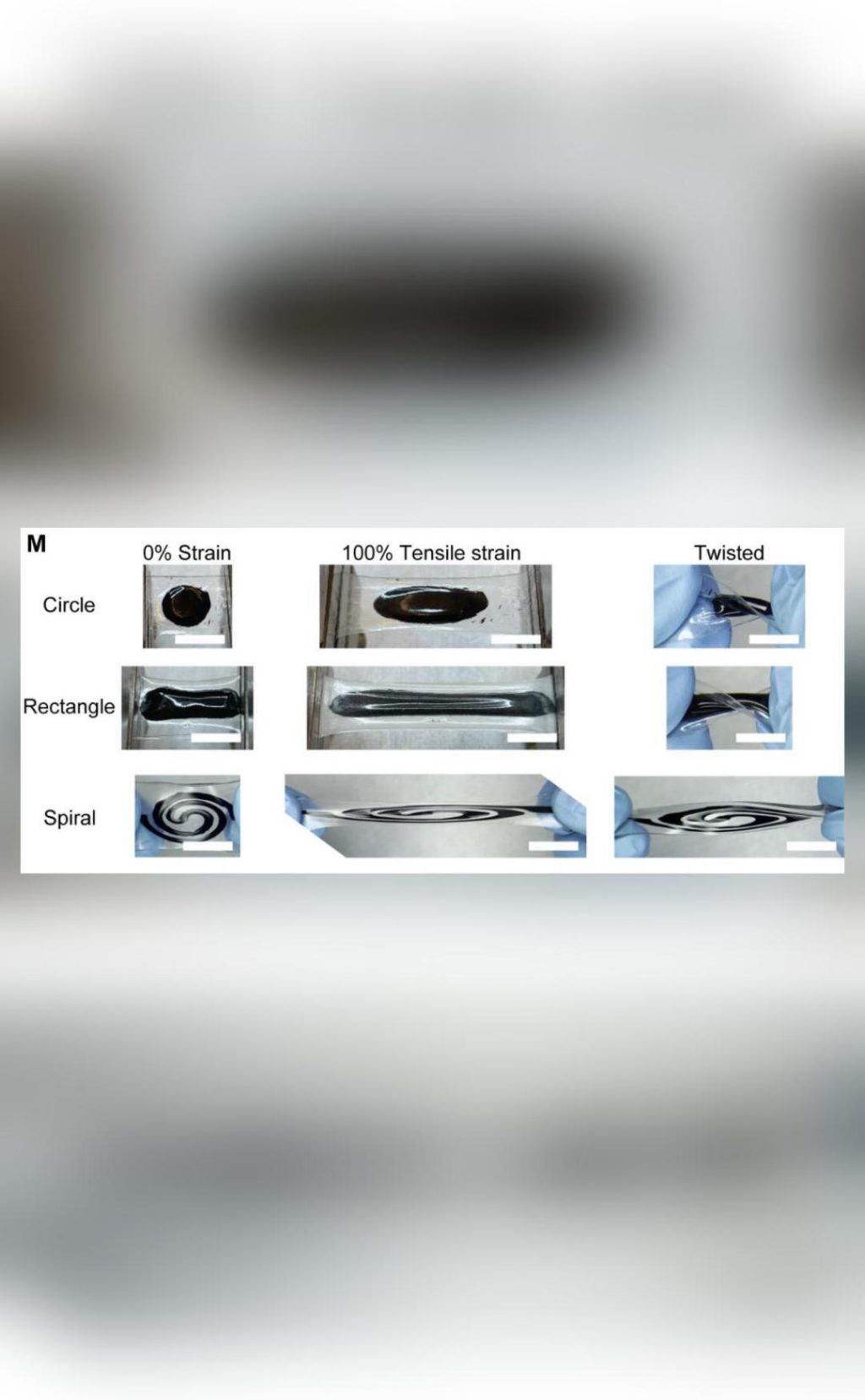
The material can be used in a 3D printer to shape the battery as you please, making it ideal for a wide range of applications. According to Rahmanudin, “The material can be used in a 3D printer to shape the battery as you please. This means that the battery can be designed to fit specific needs, such as powering a small device or being used in a particular environment.”
One of the key advantages of this new battery material is its ability to be molded into complex shapes. Traditional batteries are often limited in their shape and design, which can make them difficult to integrate into certain devices or environments. The toothpaste-like battery, on the other hand, can be shaped to fit specific contours, making it ideal for use in wearable devices, implants, or other applications where size and shape are critical.
Another benefit of the new battery material is its ability to be biodegradable. Traditional batteries are often made from non-renewable materials such as metals and plastics, which can contribute to environmental waste and pollution. The use of lignin and conductive plastics in the toothpaste-like battery makes it a more sustainable option, as it can be broken down and recycled at the end of its life cycle.
The researchers used a combination of computational simulations and experimental testing to develop and characterize the new battery material. They found that the material had a high electrical conductivity, making it suitable for use in a wide range of applications.
The implications of this new battery material are far-reaching, with potential applications in industries such as healthcare, consumer electronics, and renewable energy. For example, the toothpaste-like battery could be used to power implantable devices such as pacemakers or insulin pumps, or to power wearable devices such as smartwatches or fitness trackers.
In addition to its potential applications, the new battery material also has implications for the development of sustainable energy solutions. As the world continues to transition to renewable energy sources, the need for sustainable batteries that can store energy efficiently and effectively becomes increasingly important. The toothpaste-like battery, with its biodegradable and sustainable design, could play a key role in this transition.
In conclusion, the development of the toothpaste-like battery is a significant breakthrough in the field of battery technology. Its unique properties, including its ability to be molded into complex shapes and its biodegradable design, make it an attractive option for a wide range of applications. As the world continues to evolve and demand more sustainable and efficient energy solutions, the toothpaste-like battery is likely to play an important role in shaping the future of energy storage.
Source:
Rahmanudin, A., et al. “Moldable batteries based on lignin and conductive polymers.” Science Advances 6.34 (2020): eadr9010.