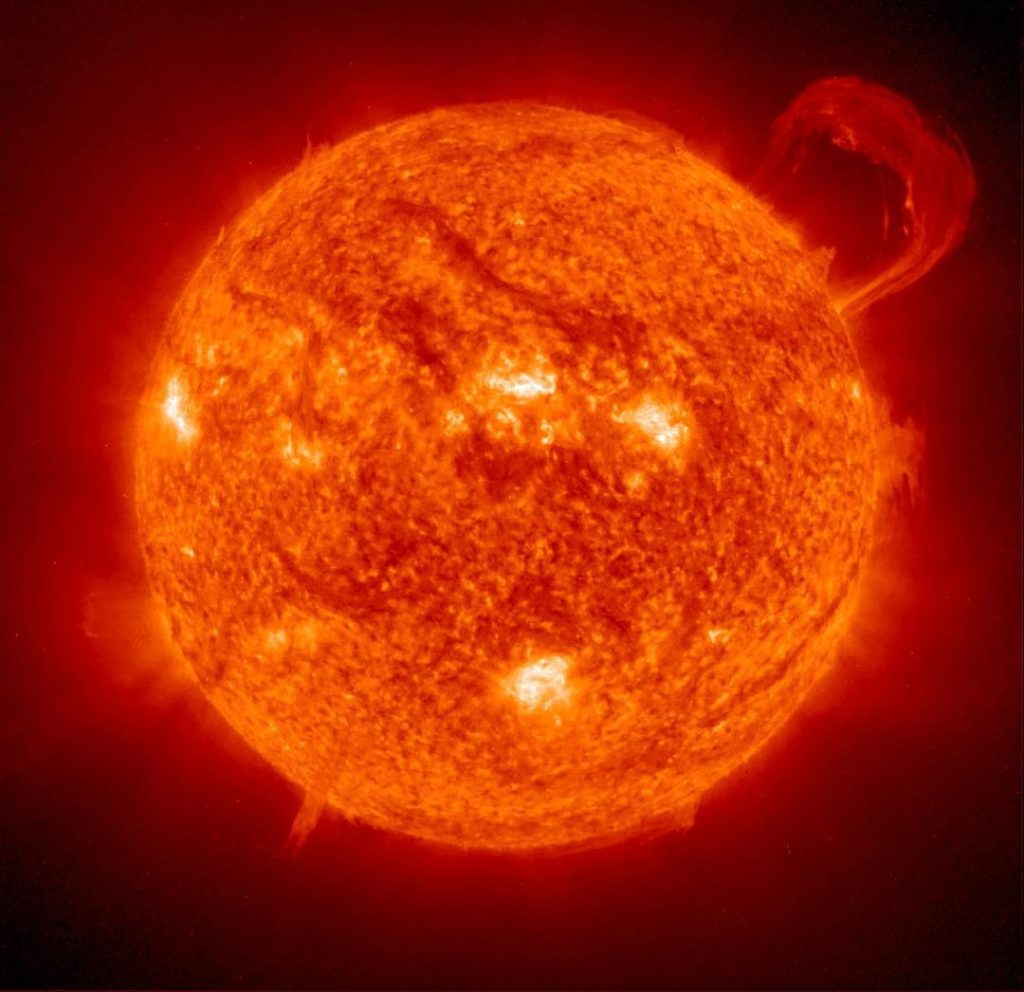
UK Scientists to Attempt Dimming the Sun: A Novel Approach to Combat Global Warming
In a groundbreaking attempt to combat global warming, UK scientists are on the cusp of launching a revolutionary experiment to dim the Sun. The ambitious project, which has been in the works for years, is expected to receive the green light from the UK government in the coming weeks. According to reports, outdoor field trials are being planned, involving the injection of aerosols into the atmosphere or the brightening of clouds to reflect sunshine.
The UK’s advanced research and invention funding agency has set aside a staggering £50 million for the project, a testament to the significant investment being made in this innovative approach. But what exactly does this project entail, and how will it work to combat the pressing issue of global warming? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the details of this bold experiment and explore its potential implications.
The Need for a Novel Approach
Global warming, caused by the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, is one of the most pressing issues of our time. The consequences of inaction are dire, with rising temperatures leading to more frequent natural disasters, sea-level rise, and devastating impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity. Despite decades of efforts to reduce emissions and transition to renewable energy, the pace of progress has been slow, and more drastic measures are needed to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Enter the concept of “solar geoengineering,” a term used to describe large-scale technological interventions designed to reduce the amount of sunlight entering the Earth’s atmosphere. This approach is seen as a potential game-changer in the fight against global warming, as it has the potential to slow down the rise in temperatures while buying time for the world to transition to a low-carbon economy.
How Will the UK Experiment Work?
The UK experiment, which is expected to begin in the coming months, will involve the injection of aerosols into the atmosphere or the brightening of clouds to reflect sunshine. The former approach, known as “solar radiation management,” involves releasing tiny particles into the stratosphere to block a small percentage of sunlight. This would have the effect of cooling the planet, potentially by up to 2°C.
The latter approach, known as “cloud brightening,” involves seeding clouds with salt or other substances to make them more reflective, thereby reducing the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface. This method is seen as a more targeted approach, as it would only affect the specific regions where the clouds are seeded.
Challenges and Controversies
While the potential benefits of the UK experiment are significant, there are also numerous challenges and controversies surrounding this approach. One of the main concerns is the potential unintended consequences of altering the planet’s energy balance. For example, changes to the global climate system could have unforeseen impacts on weather patterns, ecosystem health, and even the Earth’s magnetic field.
Another concern is the lack of international cooperation and regulation. As solar geoengineering is a global issue, it would require a coordinated effort from governments and scientists around the world to implement and monitor such a project. However, the lack of a global framework for regulating these technologies raises concerns about accountability and the potential for unintended consequences.
Conclusion
The UK’s attempt to dim the Sun is a bold and ambitious experiment that has the potential to make a significant impact in the fight against global warming. While there are numerous challenges and controversies surrounding this approach, the need for innovative solutions to this pressing issue is clear. As the world continues to grapple with the consequences of climate change, the UK experiment serves as a reminder of the importance of thinking outside the box and exploring novel approaches to addressing this global challenge.
News Source: