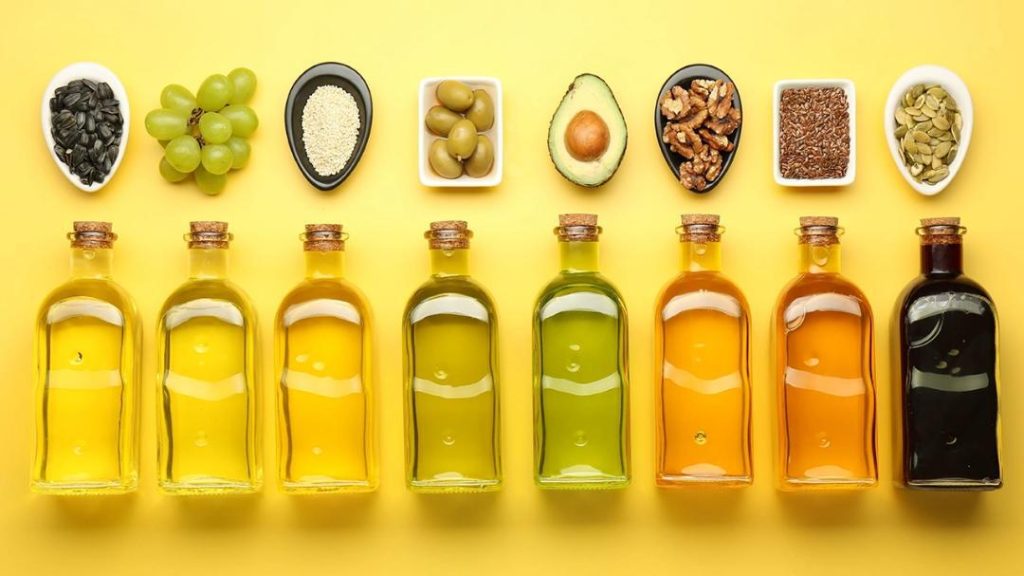
What do experts say about health hazards & benefits of seed oils?
Seed oils have been a topic of debate in the health and nutrition community, with some critics claiming that they pose serious health hazards due to their high content of unsaturated fatty acids and the use of hexane, a chemical considered hazardous in gaseous form. However, experts from top universities have debunked these myths and revealed the science behind the benefits and risks associated with seed oils.
The Concerns about Hexane
One of the primary concerns about seed oils is the use of hexane, a chemical solvent used to extract the oil from the seeds. Hexane is considered hazardous in gaseous form, and some critics argue that it can leave behind toxic residues in the oil. However, experts from Massachusetts University, including Professor Eric Decker, Food Science department, say that the amount of hexane residue in seed oil is negligible and doesn’t pose a significant health risk.
“Seed oils don’t increase acute or chronic inflammation markers,” said Professor Decker. “The amount of hexane residue in seed oil is extremely low, and it’s not a concern.”
The Health Benefits of Seed Oils
Despite the concerns about hexane, seed oils have several health benefits that make them a valuable addition to a healthy diet. These benefits include:
- High levels of omega-3 fatty acids: Seed oils, such as flaxseed oil and chia seed oil, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health and brain function.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Seed oils contain anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of conditions such as arthritis.
- High in antioxidants: Seed oils are rich in antioxidants, which can help protect against cell damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
The Risks Associated with Seed Oils
While seed oils have several health benefits, they also have some risks associated with their consumption. These risks include:
- High in calories: Seed oils are high in calories, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity if consumed in excess.
- May increase omega-6 fatty acids: Some seed oils, such as sunflower oil and safflower oil, are high in omega-6 fatty acids, which can contribute to inflammation and increase the risk of chronic diseases if consumed in excess.
- May affect gut health: Some seed oils, such as canola oil, contain trans fats, which can affect gut health and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
Expert Opinions
Experts from Ohio University, including a Food Science professor, have also weighed in on the debate about seed oils. According to the professor, seed oils do not increase acute or chronic inflammation markers, and the benefits of these oils far outweigh the risks.
“Seed oils are a healthy choice for those looking to reduce their risk of chronic diseases,” said the Ohio University Food Science professor. “They are rich in essential fatty acids, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds that can help promote overall health and well-being.”
Conclusion
Seed oils have been a topic of debate in the health and nutrition community, with some critics claiming that they pose serious health hazards due to their high content of unsaturated fatty acids and the use of hexane, a chemical considered hazardous in gaseous form. However, experts from top universities have debunked these myths and revealed the science behind the benefits and risks associated with seed oils. While seed oils do have some risks associated with their consumption, the benefits of these oils far outweigh the risks, making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Reference: