What is ‘normal faulting’, that caused the earthquake in Delhi-NCR?
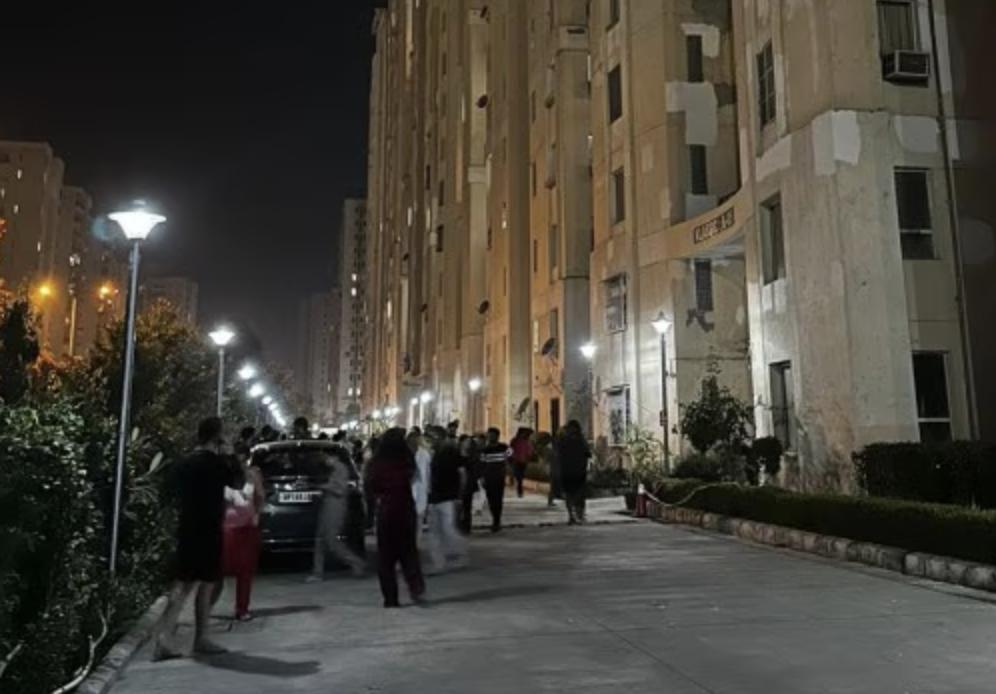
On Monday, a moderate earthquake struck the Delhi-NCR region, causing widespread panic and damage. The National Centre for Seismology (NCS) has confirmed that the quake was caused by “normal faulting”. But what exactly is normal faulting, and how does it lead to earthquakes? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of geology and explore the concept of normal faulting, which is a fundamental process that shapes the Earth’s surface.
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. These blocks can be several kilometers thick and can move relative to each other, resulting in earthquakes. In normal faulting, the block above the fault (also known as the hanging wall) moves downward relative to the block below (the footwall). This movement creates a dip, or a slope, in the Earth’s surface.
Normal faulting occurs when a block of rock is subjected to stress, which is a measure of the force per unit area. When the stress becomes too great, the rock cannot withstand it, and a fracture or fault forms. The block above the fault then moves downward, creating a normal fault.
To understand normal faulting, let’s consider a simple analogy. Imagine a stack of playing cards. If you apply pressure to the top card, it will start to bend and eventually break, causing the cards below it to move upward. Similarly, when a block of rock is subjected to stress, it can create a normal fault, causing the block above to move downward.
Normal faulting is a common process that occurs at the Earth’s surface. It’s responsible for creating many of the landforms we see today, such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus. In fact, the Himalayas, which are one of the youngest mountain ranges in the world, were formed through normal faulting.
The Delhi-NCR earthquake was a result of normal faulting that occurred at a depth of about 10 km. The NCS said that the earthquake had a magnitude of 4.5 and was centered in the Haryana region. The fault that caused the earthquake is known as a “normal fault”, which is a type of fault that occurs when the block above the fault moves downward relative to the block below.
Normal faulting is a complex process that is influenced by several factors, including the Earth’s plate tectonics, the composition of the rocks, and the stress applied to the rocks. It’s a dynamic process that has been shaping the Earth’s surface for millions of years.
In conclusion, normal faulting is a fundamental process that causes the Earth’s surface to change. It’s responsible for creating many of the landforms we see today, including mountains, valleys, and plateaus. The Delhi-NCR earthquake was a result of normal faulting that occurred at a depth of about 10 km. As we continue to study the Earth’s surface, we can gain a better understanding of the processes that shape our planet.
News Source:
https://repository.inshorts.com/articles/en/PTI/31f37e63-4ba0-4667-a617-88eaedf2cc17